The lymphatic framework is a vascular organization of pipes and channels that gather, channel, and return lymph to the course. Lymph is a reasonable liquid that comes from blood plasma, which leaves the veins at the slim beds. This liquid turns into the interstitial liquid that encompasses the cells. Lymph contains water, proteins, salts, lipids, white platelets, and different substances that should be gotten back into the blood. The essential elements of the lymphatic framework are to eliminate and restore interstitial liquid to the blood, to assimilate and return lipids to the blood from the intestinal system, and to channel liquid from microorganisms, harmed cells, cell garbage, and disease cells.
Read more here
Lymphatic framework structures
The significant parts of the lymphatic framework incorporate lymph, lymphatic vessels, and lymphatic organs that contain lymphoid tissue.
Lymphatic vessels
Lymphatic vessels are structures that assimilate the liquid that flows from the vein vessels to the encompassing tissues. This liquid is guided towards the lymph hubs to be separated and ultimately reenters the blood flow through veins situated close to the heart. The littlest lymphatic vessels are called lymphatic vessels. The lymphatic vessels meet up to shape the bigger lymphatic vessels. Lymphatic vessels from various regions of the body union and structure bigger vessels called lymphatic trunks. The lymphatic trunks converge to frame two huge lymphatic pipes. The lymphatic channels return lymph to the flow by depleting lymph into the subclavian veins in the neck.
Read more about What Type Of Wave Is Light
Lymph hubs
Lymphatic vessels convey lymph to the lymph hubs. These designs channel the lymph of microorganisms like microbes and infections. Lymph hubs likewise sift through cell squander, dead cells, and malignant growth cells. Lymph hubs contain resistant cells called lymphocytes. These cells are fundamental for the advancement of humoral insusceptibility (safeguarding cells before disease) and cell-interceded resistance (safeguarding cells after contamination). Lymph enters a hub by means of afferent lymphatic vessels, and channels, as it goes through diverts in a hub, called a sinus, and leaves the hub through an efferent lymphatic vessel.
Thymus
The thymus organ is the principal organ of the lymphatic framework. Its essential capability is to advance the improvement of explicit cells of the invulnerable framework called T-lymphocytes. When fully grown, these cells pass on the thymus and travel through veins to the lymph hubs and spleen. T-lymphocytes are liable for cell-intervened resistance, which is a safe reaction that includes the initiation of specific invulnerable cells to battle disease. Notwithstanding resistant capability, the thymus likewise creates chemicals that advance development and development.
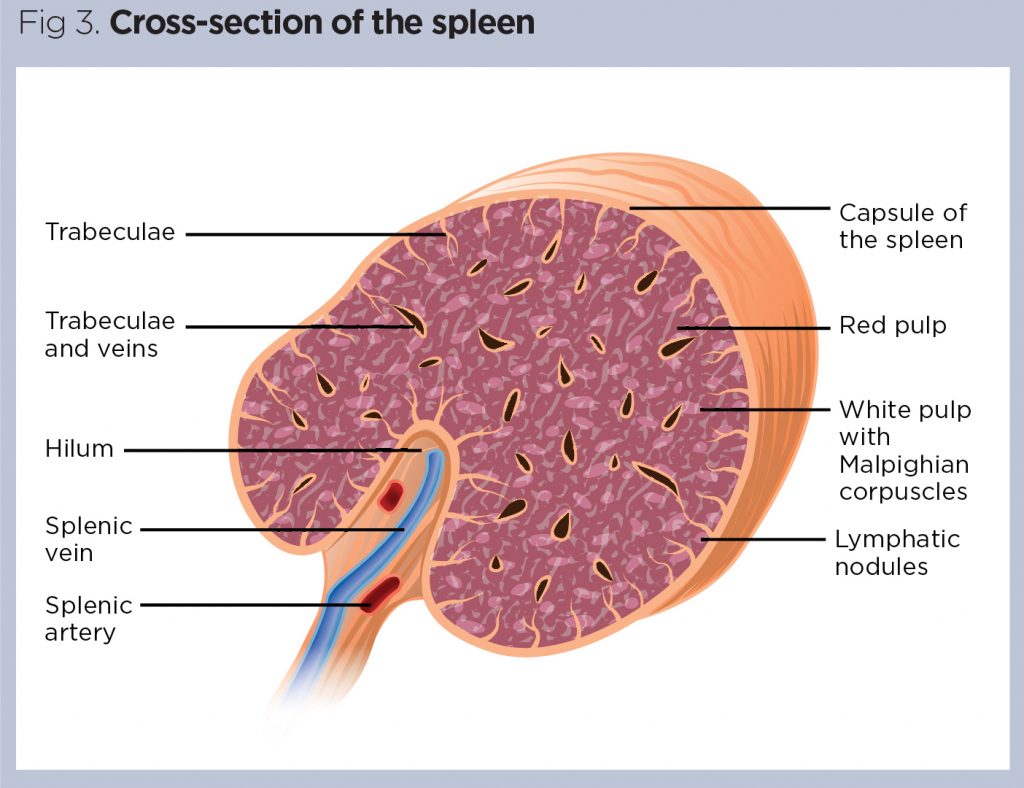
Spleen
Its essential capability is to channel the blood of harmed cells, cell trash, and microorganisms. Like the thymus, the spleen houses and aids the development of lymphocytes. Lymphocytes obliterate microbes and dead cells in the blood. The spleen is loaded up with blood provided through the splenic corridor. The spleen likewise contains efferent lymphatic vessels, which divert lymph from the spleen and toward the lymph hubs.
Tonsils
Tonsils are varieties of lymphatic tissue situated in the upper throat district. Tonsils contain lymphocytes and other white platelets called macrophages. These invulnerable cells safeguard the gastrointestinal system and lungs from sickness-causing specialists that enter the mouth or nose.
Bone marrow
Bone marrow is the delicate, adaptable tissue seen inside the bone. The bone marrow is answerable for the development of platelets: red platelets, white platelets, and platelets. Bone marrow undifferentiated organisms assume a significant part in resistance as they produce lymphocytes. While some white platelets mature in the bone marrow, a few sorts of lymphocytes relocate to lymphatic organs, like the spleen and thymus, to develop into completely working lymphocytes.
Lymphatic tissue can likewise be tracked down in the different regions of the body, like the skin, stomach, and small digestive tract. Lymphatic framework structures are spread over most regions of the body. An eminent exemption is the focal sensory system.
lymphatic framework outline
The lymphatic framework assumes a significant part in the appropriate working of the body. One of the significant jobs of this organ framework is to eliminate the overabundance of liquid encompassing tissues and organs and return it to the blood. The arrival of lymph into the blood keeps up with ordinary blood volume and strain. It forestalls edema, and overabundance collection of liquid around the tissues. The lymphatic framework is likewise a part of the invulnerable framework. In that capacity, one of its fundamental capabilities includes the turn of events and the flow of safe cells, especially lymphocytes. These cells annihilate microbes and safeguard the body from sickness. What’s more, the lymphatic framework works related to the cardiovascular framework to channel the blood of microbes through the spleen, prior to getting back to dissemination. How does the lymphatic framework work withthe stomach related framework also to retain and return lipid supplements to the blood?